Fundamentals of Traditional Chinese Medicine(TCM)
Yin and Yang –A Fundamental Theory to TCM
The theory of Yin and Yang is fundamental to the practice of TCM in diagnosing and treating health issues. Yin and Yang are used to describe the opposite qualities or manifestation regard Qi. If Yin is formed, and then Yang will be functional. If Yin is material, and then Yang is immaterial.
The relationship between Yin and Yang cannot be isolated, which means that Yin and Yang create each other, control each other, and transform into each other. From the Traditional Chinese Medicine perspective, when Yin and Yang are unbalanced in your body for prolonged periods, this can cause some health problems. TCM is seeking to understand and facilitate Yin and Yang back into balance.

Qi (life Force)—vital substance regard TCM
Qi (Pronounced “Chee”), the meaning of Qi in TCM has two aspects. One refers to the vital substances comprising the human body and maintaining its life activities, such as water and food (material essence), and breathing. The other refers to the physiological functions of viscera and bowels, channels and collaterals, such as heart, lung, spleen and stomach, Take for an example, deficient Spleen can result in unbalanced Qi which can cause the body is unable to hold the blood, and then resulting in hemorrhages.
Qi has five major functions in the human body:
- Promoting action 2. Warming action 3. Defending action 4. Consolidating 5. Promoting metabolism and transformation

Blood (Xue)– vital substance in TCM
Blood in Chinese Medicine is not the same as what western medicine describes. Chinese Medicine does not study the human body at a cellular level, but TCM focuses on the body as a whole. Regard Traditional Chinese Medicine, it is said that Qi is the active force in the moving Blood. In another word, Blood is the mother of Qi. Qi gives life and movement to Blood. At the same time, Blood nourishes the Organs to produce Qi.
The function of blood are as below:
- Providing nutrients for organs, tissues and meridians
- Maintaining healthy body movement and sensation.
- Aiding the mind and mental activities.
According to Traditional Chinese Medicine theory, blood stagnation or blood deficiency is the cause of diseases, for example, the deficiency of blood results to poor memory and insomnia, and in serious cases which could cause mental disorders and psychiatric diseases.
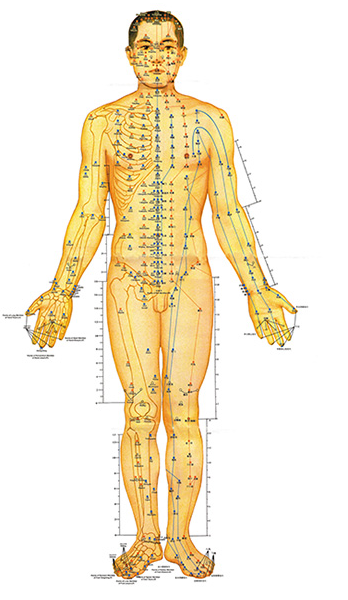
The Meridian System
The meridian System is a distribution network for the fundamental substances of Qi, Blood and Body Fluids throughout the body. There are overall twelve main meridians. Each meridian is a Yin and Yang pair, which means each Yin organ is paired with its corresponding Yang organ: the Yin Lung organ, for example, corresponding with the Yang large intestine. In addition to the 12 main meridians, there are extraordinary meridians which are not directly linked to the main organs but have various specific functions.
Meridians is active the human body between the interior and the exterior. Meridians are the collection of acupuncture points. Working on points from the surface of the body will affect what happens inside the body by changing the activity through the meridian. Sickness can occur while there is a blockage between the meridians and the Qi (Life force) when they cannot flow freely.
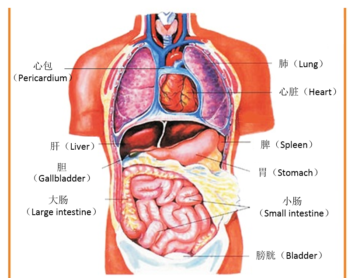
The ZANG -FU Theory (organs )
According to TCM Theory, the ZANG-FU is simply an expression to describe the 12 major internal organs of the human body. The ZANG organs include heart, lung, liver, kidney,spleen and pericardium, also known as Yin organs. The Fu organs include gallbladder, small intestine, stomach, large intestine, bladder. The functions of Zang organs are mainly to manufacture and store essence of Qi, Blood and Body fluid. The functions of Fu organs are mainly to receive, digest food, absorb nutrient substances, transmit and excrete waters. In TCM, Zang organs and Fu organs are harmonized and balanced. If Zang organs and Fu organs are inharmonious and unbalanced, resulting in health problems, for example, if liver and spleen are inharmonious, abdominal distension and diarrhea will occur.