Fertility Support
 What is Infertility
What is Infertility
Infertility refers to a couple has 1 year of regular intercourse without contraception and has been unable to conceive, or the woman is older than 35 years older after at least six months without contraception.
How acupuncture and Chinese Herbs can help
The treatment of infertility and other gynecological problems has been documented in Traditional Chinese Medicine since the ancient times. Modern science has shown that acupuncture and Chinese herbs can help to treat infertility by increasing blood flow to the pelvic region, regulating the reproductive hormones to improve ovarian and follicular functions, minimizing the adverse effects of IVF treatment, creating a thick enough uterine lining that can hold the implanted embryo, reduce the changes of miscarriage, and improved the quality and quantity of fertile cervical mucus.
Common causes of Infertility
The most common causes of infertility include poor egg quality, fallopian tube damage/blockage and adhesions, spastic tubes ovulation problems, Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome(PCOS), frequent miscarriages, endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory diseases, premature ovarian failure, luteal phase defect, and elevated FSH (follicular stimulating) male factors contributing to infertility.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is described as the abnormal growth of endometrial tissue outside the endometrium. Endometrial cells are those that are fund in the uterine lining. When those cells are fund in areas outside of the uterus (ovaries, fallopian tubes, ligaments supporting the uterus, cervix, the vaginal-rectal space, colon and bladder wall), the diagnosis of endometriosis is made. The misplaced endometrial tissue (endometriosis implants) also responds to oestrogen and follows a monthly cycle. They grow, break down and bleed with each menstrual cycle, but they cannot leave the body via menstruation. As a result, the monthly bleeding in this tissue leads to inflammation, scarring, adhesion and distortion of normal pelvic anatomy.
The most common symptoms of endometriosis include dysmenorrea, pathological uterine bleeding, associated with back pain or severe abdominal cramping, painful intercourse, painful intestinal upset or urination during the menstruation, and the inability to become pregnant.
Endometriosis is classified as to its severity.
Mild endometriosis: implants are small, flat patches of endometrial tissue growing outside of their normal location.
Moderate endometriosis: includes “chocolate cysts” of endometriosis may be smaller than a pea or larger than a grapefruit, located within the ovary.
Severe endometriosis: in some cases, bands of fibrous scar tissues (adhesions) bind the pelvic organs together.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)

PCOS refers to a set of symptoms due to elevated androgens (male hormones) in females of reproductive. PCOS is one of leading causes of poor fertility.
Common signs and symptoms of PCOS include menstrual disorders such as irregular or no menstrual periods, heavy periods, acne, excess body and facial hair, pelvic pain, mood disorders and obesity.
Diagnostic criteria is based on two of the following three findings: no ovulation, high androgen levels, and ovarian cysts demonstrated on ultrasound.
Chinese Medicine seeks to redress the unbalanced hormones. Treatment will be based on differentiations such as Kidney Yang/ Kidney Yin deficiency, spleen Qi deficiency, Phlegm dampness, liver depression/ depressive heat, blood stasis.
The study found that acupuncture treatment can regulate menstrual cycles, reduce androgen levels and reduce waist circumference.
Premature Ovarian Failure (POF)
POF is a disorder affecting the ability of a women’s ovaries to function correctly. POF is also known as Primary ovarian insufficiency (POI) that characterized by absence of menstrual bleeding, low estrogen levels, abnormally high levels of FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) and possible onset of autoimmune disease in woman younger than 40 years. The disorder is not permanent in all women. Remission of the disease is possible.
Causes of POF
In many cases, a cause for POF cannot be found. Causes include genetic and chromosomal defects, a history of chemotherapy or radiation treatment. There are also autoimmune causes of POF. In these cases, the immune system attacks endocrine organs including the ovaries, thyroid and adrenal glands.
Symptoms of POF
Amenorrea (an absence of a normal menstrual period), Estrogen deficiency (women with POF experience some symptoms of menopause including hot flashes, night sweats, sleep disturbance, and vaginal dryness). Other symptoms may include mood swings, energy loss, painful sex and bladder control problems), Infertility (women who has POF have a significantly lower chance of getting pregnant compared to women without POF. However, remissions and spontaneous pregnancies can occur).
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease(PID)
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) refers to the inflammation of the female pelvic organs or tissues.
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), PID is the invasion of damp-heat and toxins causing Blood stasis in the lower-jiao (the part of the body cavity below the umbilicus where include bladders and bowels). The most common symptoms of PID are lower abdominal discomfort or pain, abnormal vaginal discharge. If symptoms are not treated early and properly, PID can lead to inflammation of fallopian tubes, ovarian obstructions and adhesions, which is leading to infertility. Women with PID are also at higher risk of having an ectopic pregnancy.
Other factors involved in causing infertility include:
·Luteal phase defect(LPD)
·Frequent miscarriages
·Polycystic ovarian syndrome
·Elevated FSH (follicular stimulating hormone)
·Scarring and adhesions from prior surgery
·Fibroids
·Male factors contributing to infertility
Understanding the menstrual cycle
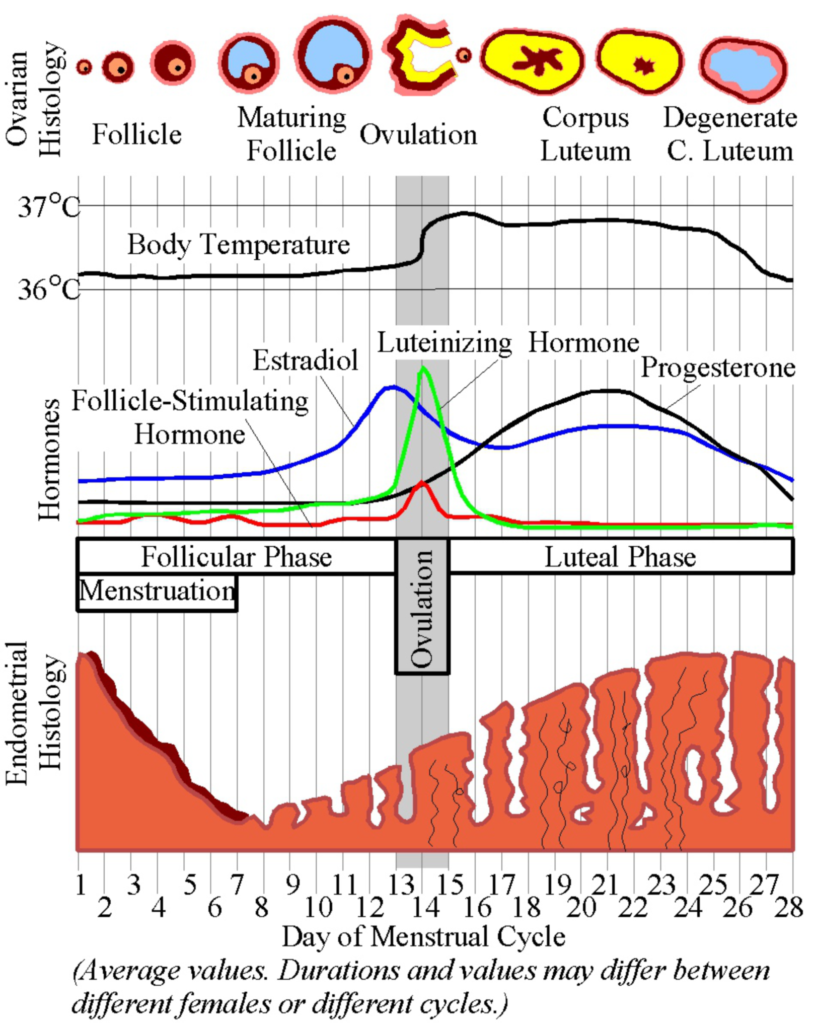
Awareness of your body always gives you power. Woman’s monthly cycle stars on the first day of the menstrual period and ends the day before the next period. On average, an ideal cycle is regular and a woman’s cycle last 28 day. However, this is common for women to experience cycles that last anywhere from 20 to 40 days due to natural variation in the duration of the follicular phase, factors such as stress, extreme emotion, weight changes, excessive physical activity and travelling can also cause irregularities in a women’s menstrual cycle.
The purposes of understanding the menstrual cycle include:
·To know your ovulation date for calculating your fertile days, thus improving your chances of falling pregnant.
·Changes to your periods, or irregular periods, are often the first signs of hormonal imbalance.
·The menstrual cycle is a key window into your overall state of health. In addition, changes in menstrual cycle can reflex other health conditions such as thyroid, metabolic disorder, endocrine disorder and immune disorder.
Knowing your cycle allows you to encourage each phase to perform optimally
The menstrual cycle is divided into three distinct phases: the follicular phase, ovulation and luteal phase.
Follicular phase
The follicular phase starts on the first day of menstruation and ends with ovulation. This is the phase in which follicles grow and one follicle becomes dominant. In the early follicular phase, after menstrual flow has ended, the lining of the uterus (endometrium) is at its thinnest and the levels of estrogen and progesterone are low. This triggers the pituitary gland to release follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). This hormone stimulates the ovaries to produce follicles. As they mature, estrogen is produced, causing the lining of the uterus to thicken in preparation for the possible implantation of a fertilized egg. Due to the rise of estrogen, it causes the cervical mucus to become clear, stretchy and have the consistency of raw egg white. A substantive discharge means increased fertility because it facilitates pathways for sperm to enter the uterus. This discharge is considered yin in nature. If you are lacking this type of cervical discharge, you might be yin deficient. Some western medicines dry up or interfere with cervical fluid such N-SAIDS, antihistamines and antidepressants.
Ovulation
Ovulation refers to the release of a mature egg from the ovary. The peak of estrogen that occurs at the end of the follicular phase triggers a sudden increase in another hormone call LH (luteinizing hormone). This LH surge triggers ovulation, where an egg is released from the ovary. Ovulation normally occurs 24 to 36 hours after the LH surge, which is why LH is a good predictor for peak fertility. Following ovulation, the egg enters the fallopian tube to make its way towards the uterus. The egg will disintegrate within 24 hours if fertilization does not occur.
Ovulation occurs 12-16 days before the next period. Usually an egg only survives for up to 24 hours, however sperm can remain active about five days. Therefore, the total duration of fertility, taking into account the lifetime of both the sperm and the egg, is about 6 days.
Luteal phase
Luteal phase follows ovulation until the start of the next menstrual period. The luteal phase is named after the corpus luteum. The corpus luteum is what remains of the follicle after the egg is released. The function of corpus luteum is to release large amounts of progesterone and some estrogen. These hormones help to thicken the lining of the uterus for the implantation of a fertilized egg. In addition, Progesterone make the basal body temperature (BBT) of the body to rise slightly until the onset of the next period. This rise in temperature can be plotted on a graph provide an approximate indication of when ovulation has occurred
If fertilization takes place, the corpus luteum continues to produce estrogen and progesterone for much longer until the placenta is mature enough to support the developing embryo. If fertilization does not take place, levels of estrogen and progesterone decrease and the corpus luteum will break down after 12-14 days. Therefore, the thick uterine lining starts to break down and menstruation to begin.
Note: Once you begin to bleed, Traditional Chinese Medicine says that you are most deficient and are vulnerable. To avoid excessive depletion while you are bleeding, keep your feet warm, and don not swim and shower in cold water. While you are bleeding and right after, it is important to nourish your blood.
To increase your chance of pregnancy you need to know the ways of finding out when you are ovulating:
Charting Your Menstrual Cycle
This is done by counting the number of days from the beginning of one menstrual cycle to the next.
To determine when you ovulate, count back 12-16 days from the next expected period.
Basal Body Temperature(BBT)
BBT is your morning body temperature before you get out of bed. Your basal body temperature will increase, typically between 0.5 and 1.0degrees as a response to hormone level changes. Each morning, take your temperature with a basal thermometer and record it on an ovulation calendar. You are most fertile on the day of the temperature spike and on the few days before.
Cervical Mucus
Cervical mucus can provide clues to your ovulation date. Cervical mucus changes throughout your cycle, during ovulation, your cervical mucus looks like raw egg whites, and becomes wet, slippery, thin, clear, and stretch. You are likely ovulating when you can stretch it a few inches without breaking.
Ovulation Predictor Kits(OPK)
Ovulation kits are available to help you determine when you are ovulating. Depending on the type of urine-based OPK, you will either collect your urine in a cup or hold a stick in your urine stream, then wait for the result of whether or not the LH surge is occurring. Don’t test your urine as soon as you wake up because you may miss the first day of your LH surge.






